
Goods & Service Tax (GST)

Goods & Service Tax (GST) Registration
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a tax on goods and services consumed in India. GST is an indirect tax that has replaced many other indirect taxes in India, such as excise duty, VAT, and services tax. GST has been in force from 1st July, 2017 based on the Goods and Service Tax Act passed by the Indian Parliament on March 29, 2017.
Goods & Service Tax (GST) Registration
A ‘taxable person’ under the GST Act is someone who conducts business in India and is registered or needs to be registered under the GST Act. A taxable person can be an individual, HUF, company, firm, LLP, an AOP/ BOI, any corporation or Government company, body corporate incorporated under the laws of a foreign country, co-operative societies, local authorities, governments, trusts, or artificial juridical persons.
GST Registration Turnover Limit
GST registration can be obtained voluntarily by any person or entity irrespective of turnover. GST registration becomes mandatory if a person or entity sells goods or services beyond a certain turnover.
Service Providers:
Any person or entity who provides service of more than Rs.20 lakhs in aggregate turnover in a year is required to obtain GST registration. In special category states, the GST turnover limit for service providers has been fixed at Rs.10 lakhs.

Goods Suppliers
As per notification No.10/2019 any person who is engaged in the exclusive supply of goods whose aggregate turnover crosses Rs.40 lakhs in a year is required to obtain GST registration. To be eligible for the Rs.40 lakhs turnover limit, the supplier must satisfy the following conditions:
- Should not be providing any services.
- The supplier should not be engaged in making intra-state (supplying goods within the same state) supplies in the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Puducherry, Sikkim, Telangana, Tripura and Uttarakhand.
- Should not be involved in the supply of ice cream, pan masala or tobacco.
If the above conditions are not met, the supplier of goods would be required to obtain GST registration when the turnover crosses Rs.20 lakhs and Rs.10 lakhs in special category states
Special Category States:
Under GST, the following are listed as special category states – Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Jammu and Kashmir, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
Aggregate Turnover:
Aggregate turnover = (Taxable supplies + Exempt Supplies + Exports + Inter-State Supplies) – (Taxes + Value of Inward Supplies + Value of Supplies Taxable under Reverse Charge + Value of Non-Taxable Supplies).
Aggregate turnover is calculated based on the PAN. Hence, even if one person has multiple places of business, it must be summed to arrive at the aggregate turnover.
Types of GST Registration
- Casual Taxable Persons:
- Non-resident Taxable Persons
- E-Commerce Operators
Benefits of GST Registration
The following are some of the advantages of GST registration:
- Bank Loans
- Supplier Onboarding
- eCommerce
- Input Tax Credit
GST Returns filing
What is GST return filing?
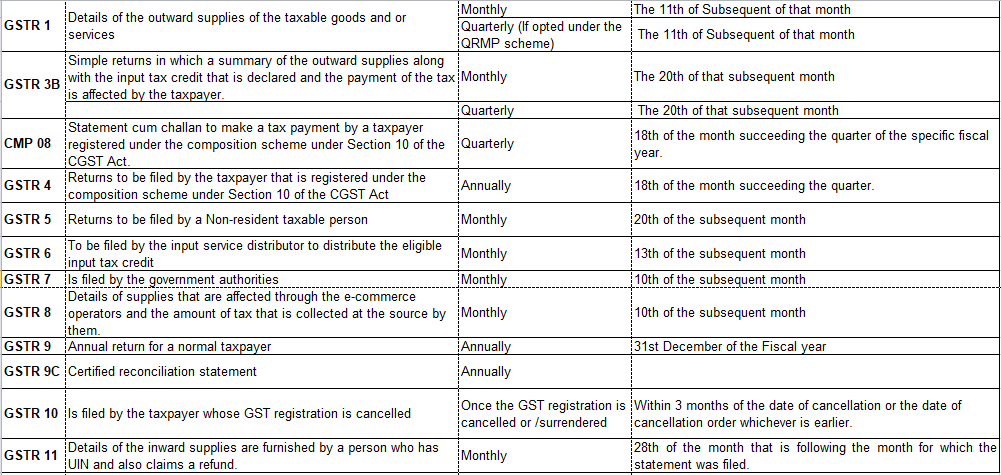
Businesses that are registered under GST have to file the GST returns monthly, quarterly, and annually based on the business. Here it is necessary to provide the details of the sales or purchases of the goods and services along with the tax that is collected and paid. Implementation of a comprehensive Income Tax System like GST in India has ensured that taxpayer services such as registration, returns, and compliance are in range and perfectly aligned.
An individual taxpayer filing the GST returns has to file 4 forms for filing the GST returns such as the returns for the supplies, returns for the purchases made, monthly returns, and the annual returns.
GST return filing in India is mandatory for all the entities that have a valid GST registration irrespective of the business activity or the sales or the profitability during the period of filing the returns. Hence, even a dormant business that has a valid GST registration must file the GST returns.
GST return is a document that contains the details of all the income or the expenses that a taxpayer is required to file with the tax administrative authorities.
Benefits of choosing us for the GST returns
- Dedicated GST Advisor
- Reminder to file GST returns
- Monthly GST Status reports
Documents Required for GST Return Filing
- Invoice
- Purchase Documents
- Bank Statement
GST LUT FILING
GST RFD-11 Form, Eligibility & Process to fill the Documents
What does LUT under GST means?
LUT in GST: Full form/meaning is Letter of Undertaking. It is prescribed to be furnished in the form GST RFD 11 under rule 96A, whereby the exporter declares that he or she will fulfil all the requirement that is prescribed under GST while exporting without making IGST payment.
Documents Required for LUT under GST
An LUT can be submitted by any individual who is registered under GST provided he has not been executed in case of tax evasion exceeding Rs.250 lakh or any other offense.
- LUT cover letter – request for acceptance – duly signed by an authorized person
- Copy of GST registration
- PAN card of the entity
- KYC of the authorized person/signatory
- GST RFD11 form
- Copy of the IEC code
- Cancelled Cheque
- Authorized letter.
GST ANNUAL RETURN FILING
What is GSTR 9: Annual Return Filing?
GSTR 9 is the annual return that is to be to be filed yearly by the taxpayers registered under GST.
GSTR 9 is to be filed yearly by the taxpayers registered under GST. It consists of details regarding the outward and the inward supplies made during the relevant financial year.
Before filing GSTR 9, the taxpayer must file all GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, or GSTR 4 returns. In case of over dues, the GSTR registration holder will not be allowed to file an annual GST annual return.
GSTR 9 consists of details regarding the outward and the inward supplies made or received during the relevant financial year under CGST, SGST, and IGST. It is a consolidation of all the monthly/quarterly returns filed in that year.
Who should file GSTR 9?
All taxpayers/taxable persons registered under GST must file their GSTR 9. However, the following are NOT required to file GSTR 9:
- Taxpayers opting composition scheme (They must file GSTR-9A)
- Casual Taxable Person
- Input service distributors
- Non-resident taxable persons
- Persons paying TDS under section 51 of CGST Act.
GST Annual Return Due Date
The due date for filing Form GSTR-9 (Annual Return) and Form GSTR-9C (Reconciliation Statement) for financial year 2022-2023 is 31st December, 2023. The Government has also decided to simplify these forms by making various fields of these forms is optional.
GST ITC RECONCILIATION
What is input tax credit?
The input tax credit is the central tax (CGST), state tax (SGST), integrated tax (IGST), or cess that is paid by a person and has a GST registration on the supply of goods or services. GST input tax includes the tax that is paid on a reverse charge basis and the IGST charged on the import of goods. But input tax does not include the tax paid on the composite taxation scheme.
The input tax credit is the tax paid by a business on the purchase and this tax is used to reduce the tax liability when a sale is made. The taxation levy is based on the value that is added at each stage of the supply chain until it reaches the consumer.
The Goods and the Service Tax Act is levied on the goods and the services based on the principle of value addition. To negate the cascading effect of the tax liability that is paid on the procurement of the raw materials, consumables, plants, and machinery, etc. This element of offsetting the tax liability is called the input tax credit.
Every person with a GST registration in the supply chain takes part in control, collects the GST tax, and remitting the amount that is collected. To avoid double taxation and the cascading effect of the tax input credit is provided to set off tax paid on the procurement of the raw materials, consumables, goods, or services that are used in the manufacturing, supply, and sale of goods or services.
The business can achieve neutrality using the input tax credit mechanism in the incidence of tax and ensure that the input tax element is not entering into the cost of production or the cost of supply of goods and services.
ITC Refunds
- Refund application preparation & filing process
- Follow up the Refund.
Under GST, the following are listed as special category states – Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Jammu and Kashmir, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
The following are some of the advantages of GST registration:
